YOUR LINGAM

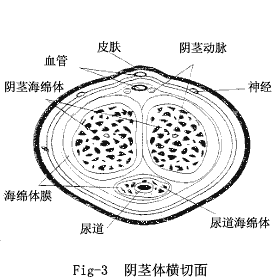
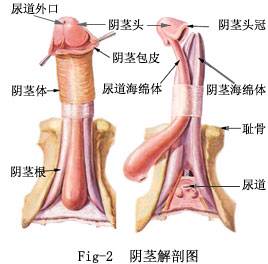
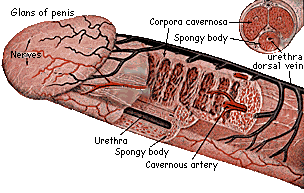
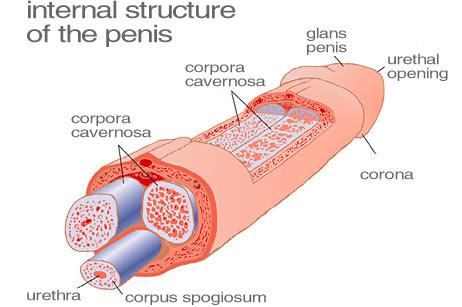
Your lingam comprises three tubes, basically: one on each side and one on the bottom, which contains the urethra and attaches to the glans, or head of the penis. (You can find diagrams in the library in a good book on human anatomy.)
Those tubes fill up with blood during an erection, and expand. How much they expand differs from person to person. With most men, the penis is smaller while flaccid and gets much larger when erect. A minority have penises roughly the same size flaccid and erect. They just get hard during an erection. Some people refer to "growers" and "show-ers."
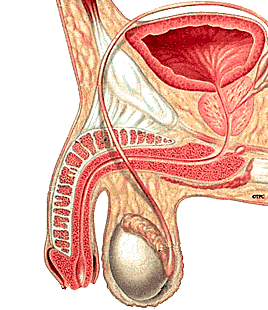
The two tubes on the sides (corpora cavernosa; singular corpus) are covered with fascia which attaches to suspensory ligaments, which in turn attach to the abdomen or the pubic bone. When you feel a little bumpiness under the skin about halfway down your penis shaft, you're probably feeling the ligaments where they attach.
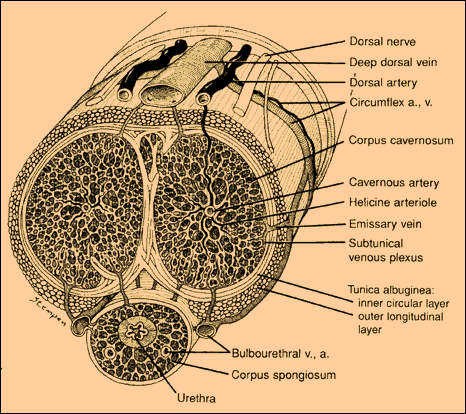
Alongside the dorsal vein on the top of the penis runs the dorsal nerve. The main problem with loop attachment devices (Ironman, JES Extender, Peni-Stretcher, Max Xtender etc) is that they tend to put the most pressure on the top of the penis, where there's the most chance of creating problems with vein or nerve.
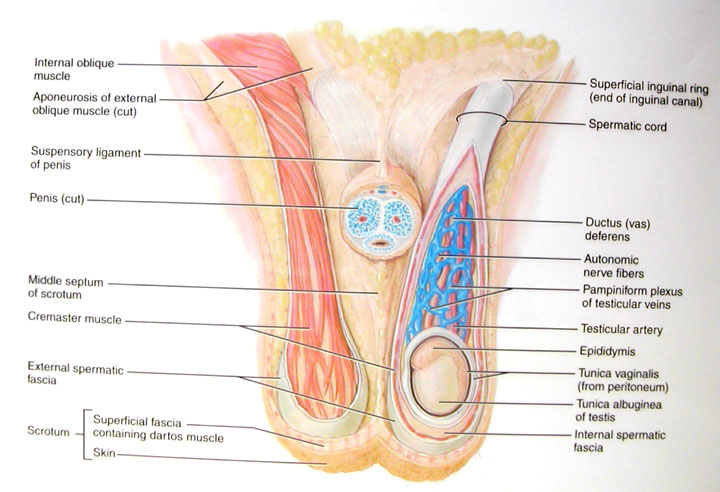
The spongy tissue of your lingam extends inside your body as well (if you've never tried it, play around behind your balls the next time you have an erection)
.
BREASTS Yes men do have them, but they are non-functioning
mammary (milk-producing) glands in men. Small muscle fibers located in the nipple
cause them to become erect when stimulated by cold temperature and sexual arousal.
For some men, they are an erogenous zone.
CHROMOSOME The genetic code or the blueprint of the human is carried in these
parts of a cell. There are 46 in humans. 45 determine what you look like and
how you function. Two determine your sex. XX means you are female. XY means
you are male.
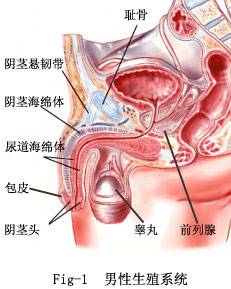
COWPER'S GLAND A gland located just below the prostate gland that secretes pre-ejaculatory
fluid to lubricate the urethra.
EJACULATE Semen-sperm mixture discharged from the body through the urethra.
Each ejaculate carries about 250-500 million sperm.
EPIDIDYMOUS The place where sperm mature. Located behind the testes.
EROGENOUS
ZONE An area of the body, that when stimulated with hands, mouth or other means
, gives sexual pleasure.
GENITALIA The External sex organs.
PENIS The external sex organ that carries the sperm-semen mixture in the urethra.
It is composed of muscles and blood vessels. When the blood vessels become engorged
and the muscles become taut in the erectile tissue of the penis, it becomes
erect. Erection is necessary to carry the ejaculate containing the sperm into
the vagina. Stimulation by hand or mouth can enhance sexual pleasure.
PITUITARY
GLAND The gland that produces the hormones FSH and LH. One of these hormones
signal the testes to produce testosterone at puberty. The other signals the
testes to produce sperm. A healthy man can produce about 1000 sperm per minute
in the seminiferous tubules.
PROSTATE GLAND A gland located at the junction of urinary bladder and urethra.
The ejaculatory ducts (the tubes transmitting the semen from seminal vesicles)
pass through the prostate to join the urethra. It is a male accessory sex gland
which adds more semen to the ejaculate. It keeps the semen from passing into
the bladder. The gland can become enlarged (called Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy
or BPH) when men get older causing urinary and erection problems. The gland
can also develop cancer in older men. When stimulated, it can give intense pleasure
in some men.
SCROTUM The sac that contains the testicles. It provides the right temperature
for sperm maturation can take place. When stimulated with hands or mouth during
intercourse, it can provide intense pleasure for some men.
SEMINAL VESICLE A sac near the bladder, behind the prostate gland, which adds
about 70% of the semen to the ejaculate to allow the sperm to swim.
SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES The specific part of the testes where the sperm are produced.
SPERM Carries one half (23) the chromosomes to make a baby. Can carry either
an an X sex chromosome, which would make a female baby, or a Y chromosome, which
would make a male baby. Men determine the sex of the baby.
SPERMATOGONIA Immature sperm cells
TESTES Also called the testicle. The male reproductive organ, located outside
the body, where sperm are formed. The plural is testicles or testis.
TESTOSTERONE The male sex hormone responsible for male sexual characteristics
such as voice deepening, body hair patterns. It is also needed for the sperm
to mature from the immature spermatagonia (the sperm cells a man is born with)
to the mature sperm capable of fertilizing an egg.
THYROID GLAND The master gland of the body. It must be working properly or your
body doesn't.
URETHRA The opening that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the
body. The same tube that carries semen and sperm to the outside of the body.
It is not part of the sexual organs but it is located in the penis.
VAS DEFERENS The tube through which the sperm travel through the glands, seminal
vesicle (to have semen added), and the prostrate. It joins the urethra as it
is passing through the prostrate gland.
A WOMANS VIEW OF THE MALE BRAIN![]()
For Asian students